Table of Contents
What is a Passive House?
Want to see a video first? Click the video-frame:
What is a passive house? Video by Dr. Wolfgang Feist
A building standard that is truly energy efficient, comfortable, affordable and ecological at the same time.
Passive House is not a brand name, but a construction concept that can be applied by anyone and that has stood the test of practice.
Yet, a Passive House is more than just a low-energy building.
- Passive House buildings allow for heating and cooling related energy savings of up to 90% compared with typical building stock and over 75% compared with average new builds. In terms of heating oil, Passive House buildings use less than 1.5 litres per square meter of living space per year – far less than typical low-energy buildings1). Similar energy savings have been demonstrated in warm climates where buildings require more energy for cooling than for heating.
- Passive House buildings are also praised for their high level of comfort. They use energy sources inside the building such as the body heat from the residents or solar heat entering the building – making heating a lot easier.
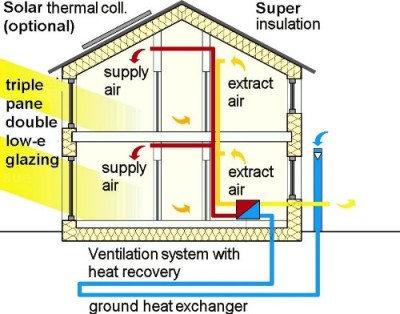
- Appropriate windows with good insulation and a building shell consisting of good insulated exterior walls, roof and floor slab keep the heat during winter in the house – and keep it out during summer.
- A ventilation system consistently supplies fresh air making for superior air quality without causing any unpleasant draughts. This is e.g. a guarantee for low Radon levels and improves the health conditions. A highly efficient heat recovery unit allows for the heat contained in the exhaust air to be re-used.
The vast energy savings in Passive House buildings are achieved by using especially energy efficient building components and a quality ventilation system: There is absolutely no cutting back on comfort; instead the level of comfort is considerably increased (see Comfort).
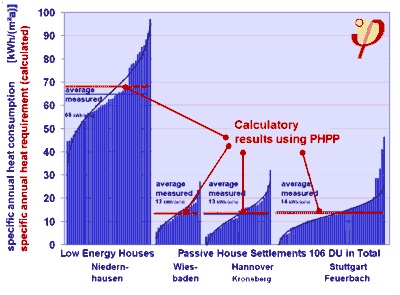 | Passive House buildings save energy and reduce greenhouse gases - not just a little but a great deal. And these savings do not only exist on paper but also in real life - passive house buildings do deliver. This diagram shows the consumption values measured in low-energy houses and in Passive House estates. The Passive House Standard is a sustainable construction standard, and the Resolution of the European Parliament of 31 Januar 2008 calls for its implementation by all member states by 2021. On 17 November 2009 the European Parliament and the Council fixed 2020 as a deadline for all new buildings to be nearly zero energy buildings. |
| Heat consumption measured in 4 residential estates: one low-energy estate (left) and three Passive House estates. Notice: No “perfomance gap” here. |
The Passive House has got it all
Comfort
The Passive House Standard offers a new level of quality pairing a maximum level of comfort both during cold and warm months with reasonable construction costs – something that is repeatedly confirmed by Passive House residents.
Quality
Passive House buildings are praised for their efficiency due to their high level of insulation and their airtight design. Another important principle is “thermal bridge free design“: the insulation is applied without any “weak spots” around the whole building so as to eliminate cold corners as well as excessive heat losses. This method is another essential principle assuring a high level of quality and comfort in Passive House buildings while preventing damages due to moisture build up.
Ecology / Sustainability
You may have been surprised by not finding ecological aspects mentioned at the very beginning of this article. Passive House buildings are eco-friendly by definition: They use extremely little primary energy, leaving sufficient energy resources for all future generations without causing any environmental damage. The additional energy required for their construction (embodied energy) is rather insignificant compared with the energy they save later on. This seems so obvious that there is no immediate need for additional illustrations. It is rather worth mentioning though, that the Passive House standard provides this level of sustainability for anyone wishing to build a new construction or renovating an older one at an affordable price – A contribution to protecting the environment. Be aware, that the principles are all published and the design tools are made available for all architects.
Affordability
Are Passive House buildings a good investment? Passive House buildings not only save money over the long term, but are surprisingly affordable to begin with. The investment in higher quality building components required by the Passive House Standard is mitigated by the elimination of expensive heating and cooling systems. Additional financial support increasingly available in many countries makes building a Passive House all the more feasible. Learn more about Passive Houses – affordability.
Measurement results
Measurements carried out in 114 Passive House apartments which were part of the CEPHEUS project showed average savings of approx. 90%; since then, lots of realized passive houses have been monitored with convincing results. In other words, the Passive House is a “factor 10 house” which only uses one tenth of the energy used by average houses. Please click here to learn about the amount of primary energy this translates to. The passive house concept delivers - the savings are real, there is no performance gap.
Versatility
Any competent architect can design a Passive House. By combining individual measures any new building anywhere in the world can be designed to reach the Passive House Standard. The versatile Passive House Standard is also increasingly being used for non-residential buildings such as administrative buildings and schools. Education on the design of passive house buildings is available on a global level with a lot of different professional trainers.
Retrofits
The Passive House Standard can also be achieved in retrofits using Passive House components. The following pages provide examples and useful recommendations on Energy savings – if you do it, do it right! (as of 30 October 2006).
Hands-on experience of Passive Houses – You have to see one to believe it
The International Passive House Open Days takes place once a year. At this event, hundreds of Passive House residents open their doors to anyone interested in getting a hands-on experience of living in a Passive House. The International Passive House Days are put on by the International Passive House Association (iPHA) and its German affiliate, IG Passivhaus.
And this is how it works
⇒ Efficiency improves comfort
The Passive House is the world leading standard in energy-efficient construction: A Passive House requires as little as 10 percent of the energy used by typical Central European buildings – meaning an energy savings of up to 90 percent. Owners of Passive Houses are barely concerned with increasing energy prices.
- The heating/cooling load is limited to a maximum of 10 W/m2
- Conventional Primary energy use may not exceed 120 kWh/(m²a) - but the future is renewable energy supply (PER) with no more than 60 kWh/(m²a). This is easy to accomplish with passive houses.
- Passive Houses must be airtight with air change rates being limited to n50 = 0.6/h.
- In warmer climates and/or during summer months, excessive temperatures may not occur more than 10 % of the time.
The Passive House is a sustainable construction concept that provides for affordable, high-quality buildings as well as comfortable, healthy living conditions. And its principles are quite easy to understand:
- As newer buildings are increasingly airtight, ventilation through joints and cracks alone is not sufficient to provide for fresh indoor air. Opening the windows as recommended won’t do the job either. Fresh air is not merely a matter of comfort but a necessity for healthy living - Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is the basic performance goal. Ventilation systems are therefore the key technology for all future residential buildings and retrofits.
- Even though ventilation systems do require an extra investment to begin with they will end up saving considerable amounts of energy costs, provided that they are highly efficient systems. Passive House quality ventilation systems will reduce the operating costs of any building.
- This is where the Passive House concept comes in: As large amounts of fresh outdoor air need to be supplied to the building anyway, why not use this air for heating? - Without any extra amounts of air, without any recirculation of air, without any inconvenient noise or drafts? This way the ventilation system pays off twice.
- This “supply air heating” concept only works in appropriately insulated buildings – that is in Passive Houses. In expert terms: The transmission and infiltration heating load must be less than 10 W/m² to make sure that the required heat can be provided by the supply air.
The Passive House – the leading concept for
Insulation
Thermal bridge free design ![]()
Airtight construction
Heat recovery ventilation
Highly insulating windows ![]()
Innovative building services ![]()
An energy balance is compiled to make sure that all these details are perfectly coordinated. This balance is established using the Passive House Planning Package (PHPP).
Examples of existing Passive Houses and their residents confirm: the Passive House concept works!
Please click here to view Passive House examples. See also: external data base on built Passive Houses
What’s the Passive House “secret“?
1) The Passive House concept doesn’t only work on paper – Built Passive House examples around the world prove that it also works in real buildings. See also: Passive House Data Base.
2) The Passive House concept has been proven to works in real life: Passive House – measurement results.
Several thousand Passive House dwellings have been monitored with respect to air quality, thermal comfort, energy consumption and construction as well as operating costs. These results have been published. The results show that the concept fully lives up to its promises: An improved level of comfort paired with extremely low energy consumption - sustainably low.
3) Passive Houses are affordable.
Building professionals in several countries with different climatic conditions and building tradiations have shown: It is possible to develop the Passive House Standard based on the existing experiences and knowledge in the building sector. All it takes is: specific know how and best practice building components (i.e. windows, heat recovery units). Passipedia is the knowledge database to dissiminate this development.
4) Passive Houses offer a maximum level of comfort.
For some 40 years the meaning of superior termal comfort has been well established on a scientific level: It was the publication of Ole Fanger in 1972: “Thermal Comfort” whose results became the basis for modern international standards on thermal comfort such as ISO 7730. The Passive House concept is based on a thorough analysis of how to achieve superior comfort levels with mainly passive components in different circumstances of the natural environment.
5) Passive Houses are sustainable.
6) Passives Houses mostly benefit regional manufacturers - everybody is invited to contribute.
Products for Passive Houses are best practise products all around the world: Minimal U-values, superior window energy performance, maximum heat recovery rates. These products are mainly produced by small and medium enterprises on a local and regional level. This is adequate for passive components, because the resources are available anywhere. Insulation materials e.g. can be produced from a lot of very different resources - the main material always being just air included in small spaces, moving very slowly. The structural material can be wool, straw, wood fibers, paper, mineral wool, several types of plastics, foamed calcium silicate, foamed glass, … This is an open development and everybody is invited to contribute.
See also
The Passive House - definition
Read the IPHA-brochure “Active for more comfort: Passive House Information for property developers, contractors and clients”