Table of Contents
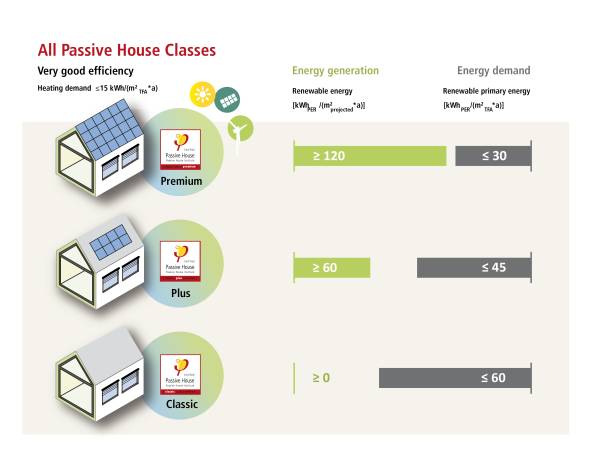
The Passive House Classes: Classic, Plus and Premium
Renewable energy is the ideal complement to the efficiency of the Passive House Standard. In order to provide guidance for this combination, the Passive House Institute offers three tiers for its building certification: Classic, Plus and Premium. They classify the building in terms of their overall efficiency level and the renewable energy generation. The classes Plus and Premium were first introduced with PHPP version 9 (2015) as addition to the well-established Passive House Classic.
The functional definition of the Passive House and EnerPHit standards remain unchanged and is the same for all three classes (relating to useful energy demand for heating and cooling, as well as airtightness and comfort criteria). The assessment of the different classes is driven by the total primary energy demand, as well as renewable energy supply. The higher the achieved level of overall efficiency and of renewable energy generation, the higher the Passive House class. The Passive House classes are assessed using the PER methodology, Primary Energy Renewable.
The classification is available for newbuild Passive House buildings, as well as for EnerPHit retrofits. In the case of EnerPHit the PER targets are adjusted slightly to account for the higher heating energy demand limits
There are different ways of achieving a higher Passive House class. This article shows details and examples of how to reach the different Passive House Classes, including explanations of how different energy supply systems are considered in the PER methodology (biomass, solar thermal etc.).
Selected case studies:
- Passive House Premium – Erne Campus, Ireland (iPHA Project Spotlight, Sept 2023)

- EnerPHit Plus – High rise office buildings in Vienna, Austria (iPHA Project Spotlight, March 2022)

- Browse implemented projects worldwide in the online Passive House Database. Use the advanced search to filter for Passive House or EnerPHit by Class Classic/Plus/Premium.
Renewable energy generation
Renewable energy generation in the context of buildings is typically assessed based on achieving a “net-zero” or even “positive” energy balance. The intention of these approaches is to generate at least as much energy as is being consumed over the course of the year in absolute terms, i.e. MWh per year. While this initially appears intuitive, this approach presents challenges and can be very misleading:
- In a “net” energy balance, effects of energy storage and distribution losses are neglected entirely. The additional energy needs to cover storage losses can, however, be quite significant (especially for heating demand, as shown by the PER methodology). For an honest “zero-energy” approach, these losses would need to be taken into account.
- It is easier to offset the absolute energy demand in the case of a single family home than it is for a multi-storey building. Multi-story buildings, however, have a lower impact in terms of space and material use and are therefore advantageous in terms of sustainable housing developments.
Instead of off-setting energy demand and energy generation, the Passive House concept rates both aspects independently of one another. The energy demand is measured against the value of the service, which is represented by the useful space of the building, the so-called “Treated floor area (TFA)”. The renewable generation is measured against the area that the building occupies and that is therefore longer available for other uses: the “Projected building footprint (PBF)”. This approach of independent assessment of the efficiency level (with respect to the living area) and the energy generation (with respect to the projected footprint area) encourages optimised solutions for both parameters. Regardless of whether the building is a bungalow or an office tower, it is ensured that the energy input needed for health and comfort is low and the energy output with respect to the locally available renewable resources is high. Bungalows will automatically become “plus-energy” houses in many cases, whilst high-rises will not be penalised for not achieving “net-zero”.


See also
Current building certification criteria including the categories Classic, Plus and Premium
"Primary Energy Renewable" (PER) - Passipedia landing page
Classic, Plus, Premium: The Passive House classes and how they can be reached
iPHA fact sheet No. 3: The new Passive House Classes based on the PER system and their implications
We welcome any questions or comments regarding the Passive House categories, PER factors or building certification criteria. Please send them to info@passivehouse-international.org.